SKIPPER APP Technical Description and User Manual
Login/Registration
Login
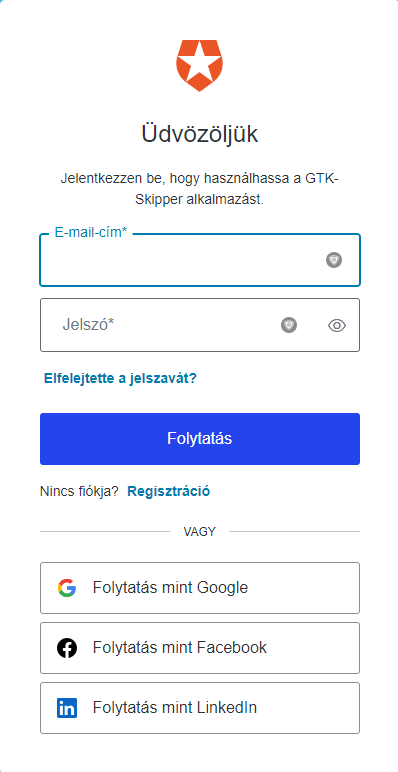
1Login
To login into the application, you can use your e-mail address and password, or you can select Google account. After successful login the application redirects you to the dashboard of Learning Paths.
Registration
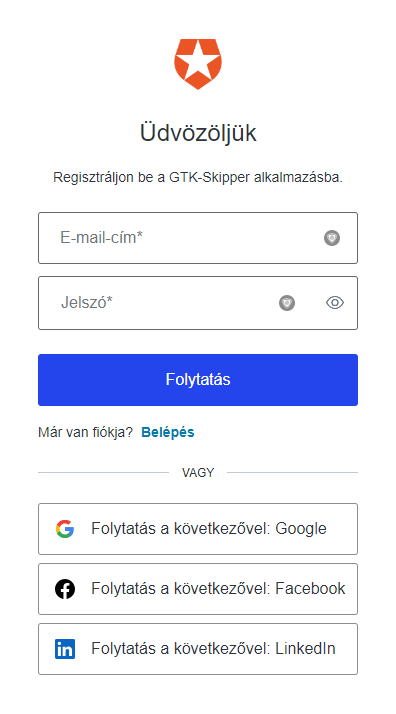
2Registration
The registration form is identical to the login form. You can register with your own e-mail address and password, or you can select your Google account. After successful registration the application asks you an account confirmation.
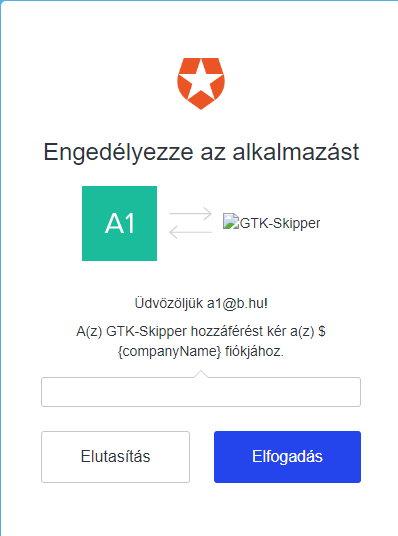
3Confirmation to finish registration
After registration complete the application logs you in and redirects you to the user profile page to fill your profile. It is very important to fill it correctly because some of data from here will be printed on the passport!
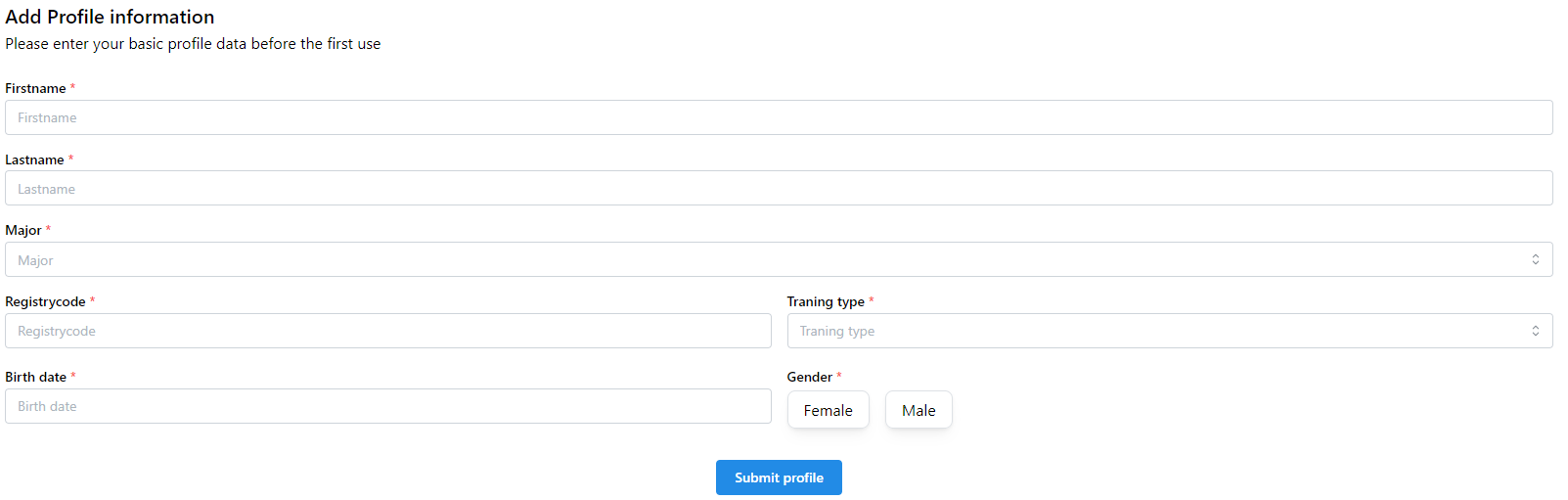
4Profile setup
Role-based functionality
Admin
The administrator can handle some system function to make sure the application works appropriately. It is very important before the first use of application the admin must do some preparation.
Institution
The admin handles the institution data. He/she adds the basic institution data, registers the faculties and majors and specify the contact information of the institution. The basic institution data come from a .csv file located in the server side. The basic data should be changed after first admin login.
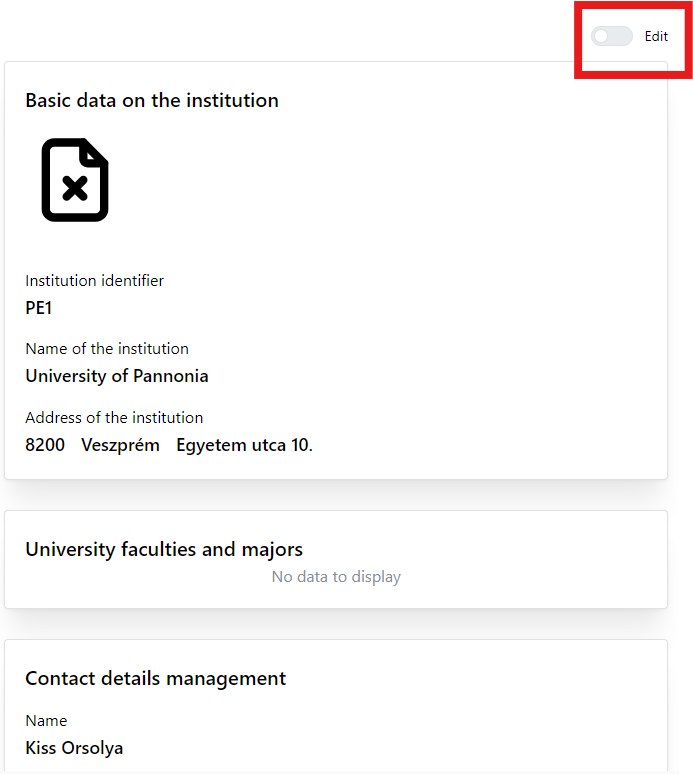
5Handling of institution
The institution page opens in read-only mode by default. To change data admin must enter into edit mode by clicking on Edit switch button.
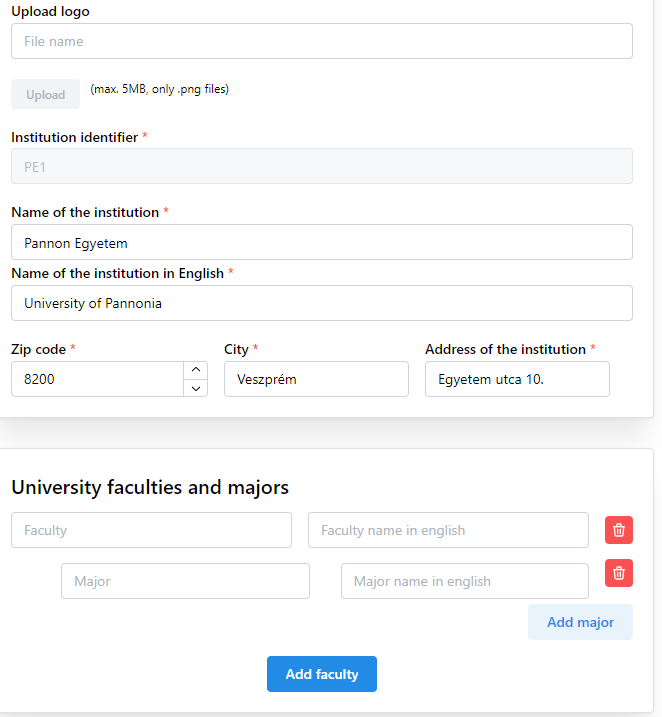
6Institution page in edit mode
During editing the name of the institution, faculties and majors must be added in English as well. This will have importance during passport generation process.
It is also important to upload an appropriate institution logo otherwise the passport generation will be disabled. The institution logo will be placed on passport.
After admin finish editing hit the save button and the data will be saved.
Mentors
On mentors page admin can handle the mentors in the system. She/he can add new mentor or remove an existing one.
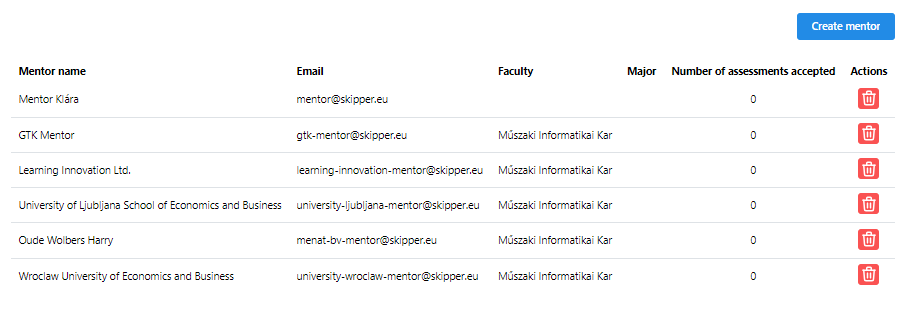
7Mentors’ list
To remove an existing mentor simply click on the red trash can icon. The system will ask for confirmation. To add new mentor click on the Create mentor button.
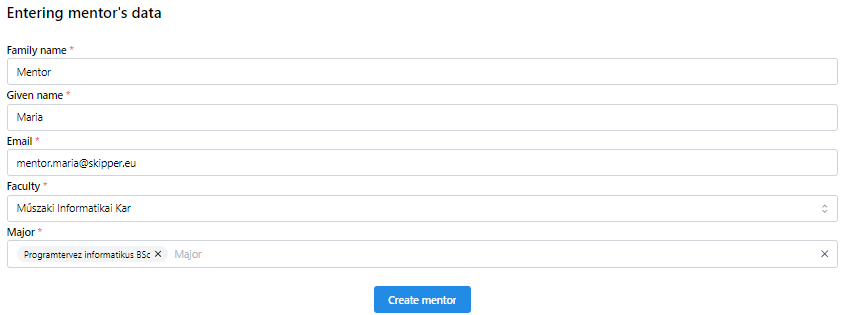
8Mentor’s data
Fill the mentor’s data appropriately and hit the Create mentor button to save entered data. After successful creation the new mentor appears in the list.

9New mentor in the list
The new mentor immediately can login and use her/his account.
Generate passport
The passport generation process can be initiated by admin on Generate passport page. There are two ways to generate passport:
-
Automatic generation
Automatic generation means the system will assign a serial number to passport automatically which is a unique identifier. The format is: Year/Serial number. E.g.: 2024/00001. To use this mode the switch button must be disabled (it is enabled by default). To start generation click on Generate button.
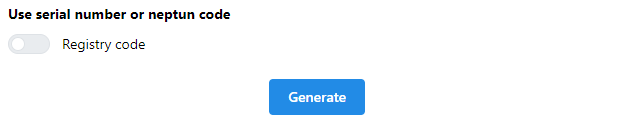
10Automatic generation by serial number
-
Template based generation
Template based generation mode is used when the institution has diploma numbers and they want to place these numbers on passports instead of auto generated serial numbers.
To use this mode please turn on the switch button and please download the template by clicking on Template button. Always use this template! This is an excel file with two columns.
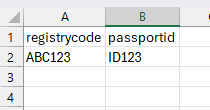
11Example template
The registry code is the student’s unique identifier in the institution. The passport id the id we want to place on passport as diploma number.
If we use template mode the Generate button will open a window where we have to select the template file to upload.
Passports are generated only for that students who have accepted self-assessment by a mentor and all required data is correctly filled in student’s profile.
When Admin generates the passports a window pops up before generation where admin can decide which language will be used for passports.
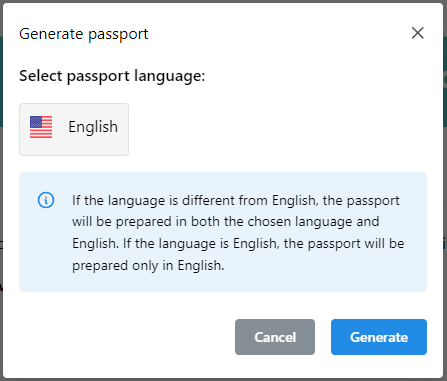
12Passport language selection
If the selected language is not English then two passports are generated. One in selected language and one in English. If English is selected only one passport is generated in English.
Student
With student account a student can perform only student related actions. These functionalities are discussed in details below.
Learning paths
After successful login the system redirects to the learning path category page. The students can select learning path categories.

13Learning path categories
To select a learning path simply click on it. A summary page opens.
14Summary page of the selected LP category
Click Next button the system opens the learning paths of selected category.
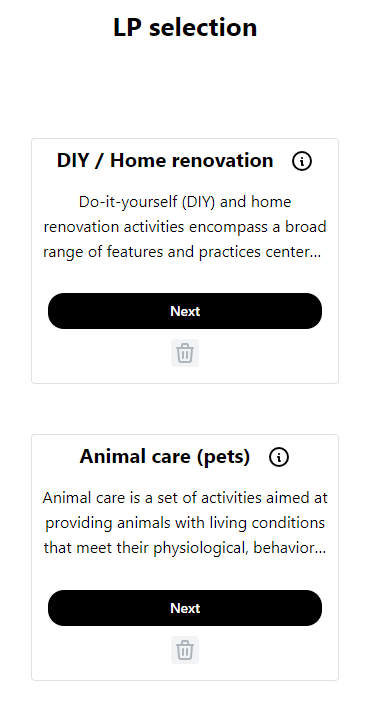
15LP list
Here students can select learning path by clicking on Next button or get detailed information about LP by clicking on the information icon on right corner. After clicking on Next button the form of the selected LP is open and students can fill it.
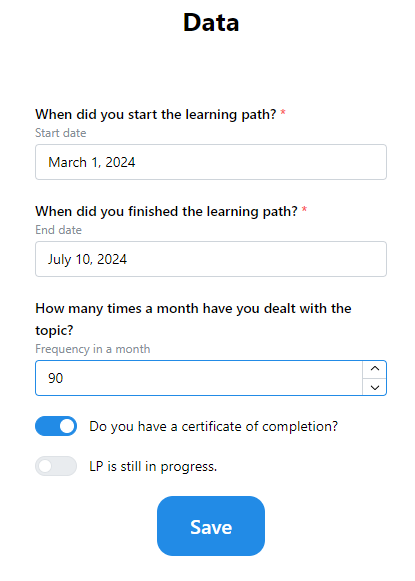
16LP form to fill
After the form is filled students can save it with Save button. Important: if user profile is not filled then the system rejects to save LP and redirects the student to profile setup page to fill the profile! After profile is filled LP can be saved.
If it was saved successfully the LP is marked as completed and can be deleted anytime.
17Completed LP
Assessments
On Assessment page a student can see the result of her/his self-assessment sent back by mentor.
-
Accepted
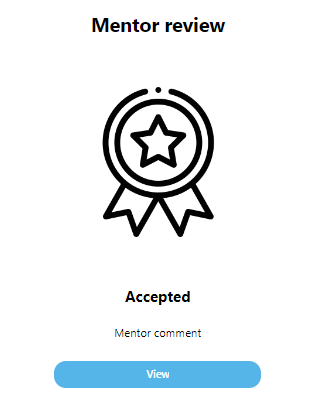
18Accepted
If the student’s self-assessment is accepted he/she can click on the View button to see the scores she/he earned.
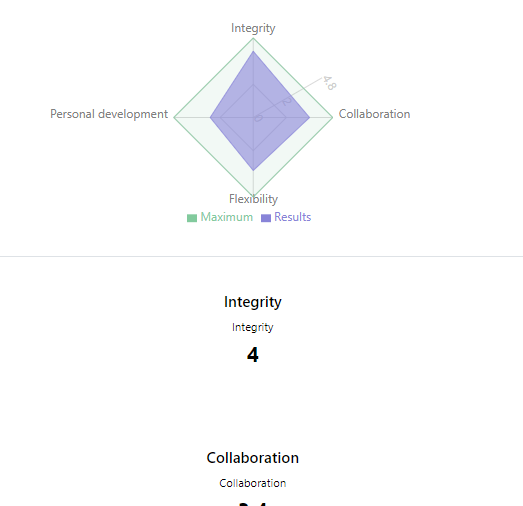
19Self-assessment scores
On the bottom of the page there is a summary table of scores as well.
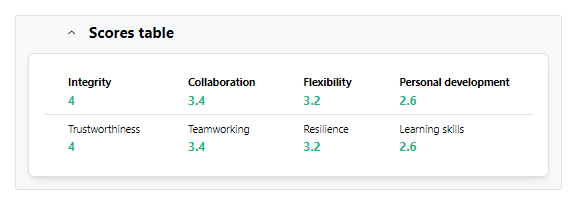
20Score table
-
Challenged

21Challenged
If a self-assessment is challenged the student has the possibility to correct the marked questions by clicking on Retry button. If she/he retries the questionnaire appears again but with only the marked questions.

22Retry
When she/he goes through the marked questions there is no mentor selection. The self-assessment is automatically sent to the original mentor who challenged it earlier.
If the mentor gets back the changed self-assessment and wants to accept it the marks on the questions must be deleted.
-
Rejected
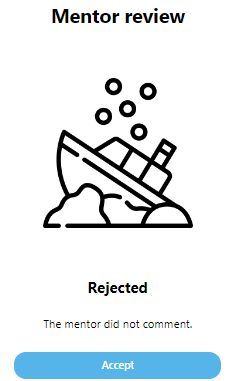
23Rejected
If the self-assessment is rejected the student can only accept it by clicking on the Accept button. If she/he does the rejected self-assessment will be deleted from the system and a new one can be started. If the rejected self-assessment is not accepted then due to the rejected is still in the system new self-assessment cannot be started.
SKIPPER Passport
Under this menu the student can see her/his passport. A student can have one or two passports in the system. If the generation language is set to different than English two passports are generated: in the selected language e.g. Hungarian and in English. If the selected language is English than only one passport is generated in English. (See language settings in Passport Generation chapter.)
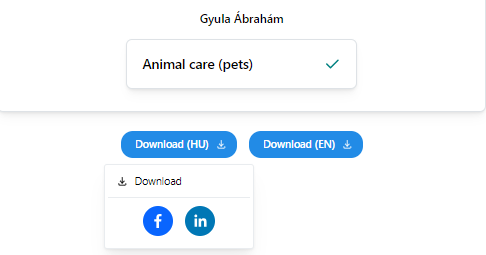
24Passports
The generated passports can be downloaded and shared on Facebook or LinkedIn. Important: the generated passports available for 1 year from generation!
Progress
On Progress page students can see the completed LPs, go back to add more LP and start the questionnaire.
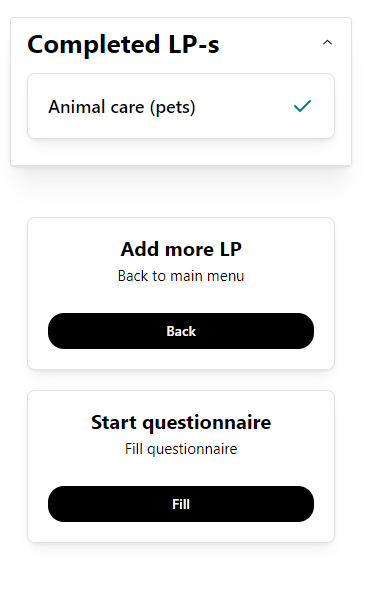
25Progress page
To start the questionnaire click on the Fill button. The system automatically loads the questionnaire.

26Started questionnaire
When you select an answer system confirms that the save was successful or not. The selected answer is highlighted with blue colour.

27Highlighted answer
If an answer is selected to go to the next question click on Next button. Or you can exit from questionnaire.
28Exit questionnaire
If you exit the questionnaire you can save it for later or delete and restart (for example at a later time).
29Progress bar
There is also a progress bar at the bottom of the page. It indicates the percentage of answered questions (25%, 50%, 75% and 100%).
If you filled the questionnaires you must select a mentor to send the whole completed questionnaire to evaluate.
30Mentor selection
To select a mentor just click on the Select button under the mentor’s name. After selection you must finish the questionnaire.
31Finish questionnaire
To finish it click on Finish questionnaire button. The questionnaire is sent to the selected mentor. After successfully submitted it to mentor the questionnaire not available anymore.
32Questionnaire is disabled
Mentor
A mentor can evaluate the sent self-assessments. After login the Request page opens.
Requests
On this page the requests can be seen which are sent by students to mentor. To select a request simply click on the request in the left-side list.
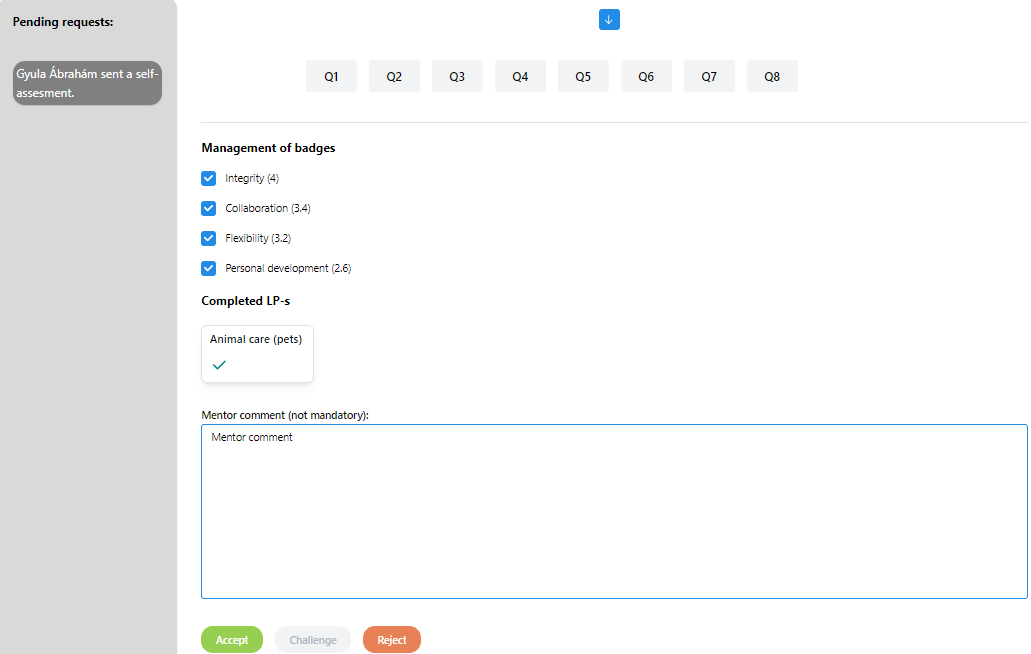
33Requests
The mentor can accept, challenge and reject the self-assessment. If the self-assessment is accepted or rejected no other information mandatory. Mentor can leave comment but it is optional.
If the self-assessment is challenged mentor must select at least one question-answer which with she/he has problem. To do this select the question from the list at the top of the page and click on Mark button. To delete mark click on Delete mark button. With Next button you can go to next question.
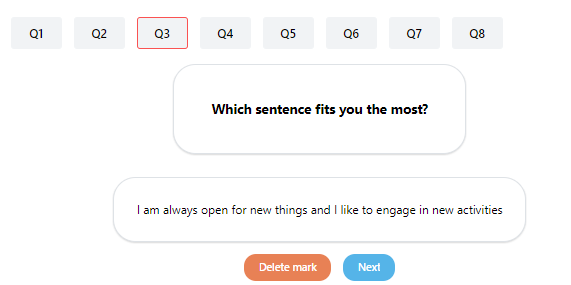
34Marked question
Of course multiple questions can be marked. If one or more question is marked the self-assessment cannot be accepted only challenge or reject.
Mentor can also specify which badges should be placed on passport by selecting or deselecting them. To do this in Management of badges section you can select or deselect badges.

35Badge selection
Only the best four badge can be managed. After each badge you can see the earned score for that badge category. If the self-assessment accepted, challenged or rejected a notification sent by email to students.
When mentor accepts, challenges or rejects the self-assessment a window opens to select the language of notification email sent to the student about review.
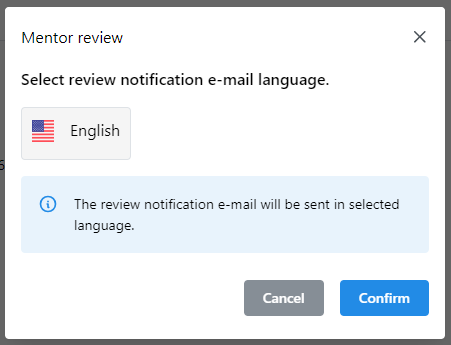
36Language selection of notification e-mail
Accepted
On Accepted page the mentor can see the accepted self-assessments so far. It is a read-only page.
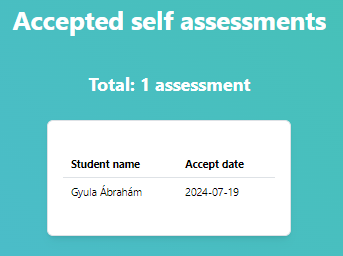
37Accepted self-assessments
General functionality
Category help
On the Category help page we can see the detailed description of questionnaire categories.
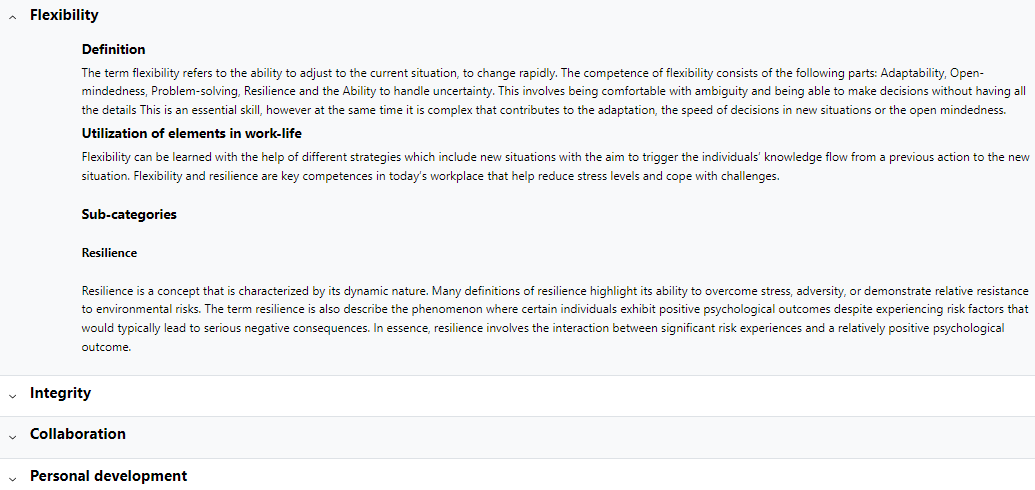
38Category help
Institution
For non-admin users the Institution page appears as exactly the same as in case of admin but in read-only mode.
Profile
On Profile page a user can change her/his profile picture, name and password or delete the account.
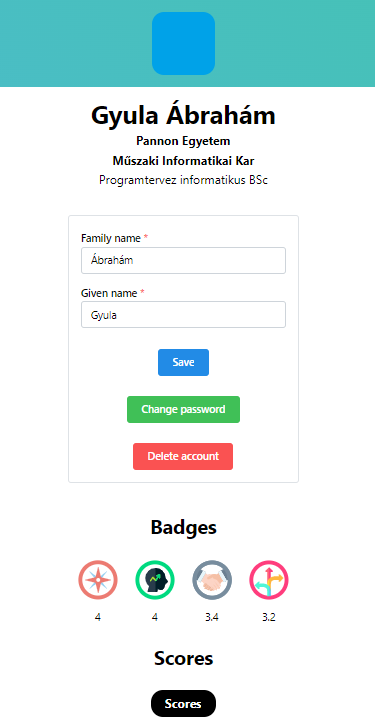
39User profile
For students the badges and scores also appear here. The Score button opens the score page discussed above. The badges are the four best badges with score values. Of course the badges and scores are not displayed in case of mentor and admin because these are student related data.
SKIPPER KNOWLEDGE BASE
Category Definitions
|
Category title |
Flexibility |
|
Category definition |
The term flexibility refers to the ability to adjust to the current situation, to change rapidly. The competence of flexibility consists of the following parts: 1. Adaptability: The ability to quickly adjust to new conditions, changes in the environment, or different ways of doing things. 2. Open-mindedness: Being open to new ideas and willing to change pre-existing notions when given new information. 3. Problem-solving: The ability to identify and implement new or unusual solutions when traditional ones do not work. 4. Resilience: Being able to deal with setbacks, criticism, and rejection, and to bounce back quickly from them. 5. Ability to handle uncertainty: This involves being comfortable with ambiguity and being able to make decisions without having all the details This is an essential skill, however at the same time it is complex that contributes to the adaptation, the speed of decisions in new situations or the open mindedness |
|
Sub-categories with definition |
Flexibility (see above) Adaptability: Adaptability is a crucial trait that makes the individual able to cope with uncertain circumstances and demanding situations. Based on the literature, adaptability can be defined as the competency to control the understanding, the emotions and the attitude towards new, unknown situations. This includes the ability to adapt and cope with uncertain circumstances well, deal effectively with the emotions and behaviors related to the unfamiliar situations. Unpredictable events allows the individuals to remain open minded to the change with quick assessment of new complex circumstances in order to formulate appropriate responses. Resilience: Resilience is a concept that is characterized by its dynamic nature. Many definitions of resilience highlight its ability to overcome stress, adversity, or demonstrate relative resistance to environmental risks. A broader perspective views resilience as the capacity of a dynamic system to withstand or recover from significant challenges that threaten its stability, viability, or development. The term resilience is also describe the phenomenon where certain individuals exhibit positive psychological outcomes despite experiencing risk factors that would typically lead to serious negative consequences. In essence, resilience involves the interaction between significant risk experiences and a relatively positive psychological outcome. |
|
List of key elements |
Flexibility Dealing with uncertainty Incorporating new information Managing change Focus on goal Adaptability Monitoring circumstances Deliberation Changing plans Resilience Self-assessment Assessment of others Situative elements Mindset |
|
Utilization of competence elements in work-life |
Flexibility can be learned with the help of different strategies which include new situations with the aim to trigger the individuals’ knowledge flow from a previous action to the new situation. The occurring barriers can hinder the skill of flexibility, so a flexible thinking is significant in order to get new perspectives and to create new ideas and strategies. That is why in order to develop the flexibility of someone coping with a mixture of tasks, new requirement adaptation to the new projects, individually and in a group can support the process. Flexibility and resilience are key competences in today’s workplace that help reduce stress levels and cope with challenges. |
|
Category title |
Integrity |
|
Category definition |
Integrity is the capacity of the self to be consistent with positive values and care for the view and beliefs of others. It also include firm choices and comprehensive knowledge of different ideas or belief systems. Integrity is a core value of a person that is shaped by family values and practices, socialization and experience, although it can be learnt and adjusted by formal university education as well. A person who is mastering integrity behaves in an ethical and fair way consistent with professional standards and rules of conduct. Demonstrates selflessness of action by doing the right thing regardless of personal and professional consequences. |
|
Sub-categories with definition |
Responsible Responsibility skill is the ability to take ownership of what you do in the workplace. Professionally define it, it could be said, responsibility is tenacity, dedication, and determination; willingness and ability to accept responsibility; commitment to the organization; sense of responsibility; capacity to become personally involved in the job Ethical approach Ethics are a set of beliefs and values that help individuals determine what actions are right or wrong based on their personal beliefs. Ethics incorporate principles and values that guide decision-making and treating people fairly and equitably. The principles of business ethics emphasize the importance of honesty, integrity, and accountability in all interactions, considering the effects of decisions and actions on stakeholders, customers, suppliers, employees, competitors, the environment, and the community. Trustworthy Trustworthiness incorporates key elements of behavior such as integrity, honesty, loyalty and keeping promises. Integrity refers to the application of ethical principles and promoting ethics in the everyday life, while honesty is more focused on credibility. Trust provides information about with whom we should share information, from whom we should accept information, and what consideration such information should be given. |
|
List of key elements |
Responsible Take ownership of what you do Capacity to self-direct Set your own targets and objectives Willingness to take additional duties Ethical approach Making fair and just decisions Treating people fairly and equitably Considering the impact on others Trustworthy Honesty Promise-keeping Loyalty |
|
Utilization of competence elements in work-life |
Ethics are generally taught in the family, through religious training in a special school, or through learning in the course of one’s life, although life experiences shape the ethical decision making the most. There are, however, core values that are common to almost all business fields, example, reciprocity (the golden rule), honesty, sincerity, compassion. In addition, many professions have codes of ethics that professionals are encouraged to follow, and help develop integrity through decisions. Integrity is also crucial in turmoil and crisis and in situations that involve long term strategic thinking. |
|
Category title |
Decision making |
|
Category definition |
In the professional world, decision-making skills are essential for success. Graduates with weak decision-making abilities may struggle to assess risks, identify opportunities, and make informed choices in their careers. Poor decision-making can lead to missed opportunities, ineffective problem-solving, and compromised performance, which can negatively impact career growth and advancement. Graduates who make poor decisions may take unnecessary risks or fail to consider potential pitfalls and negative consequences. This increases the likelihood of failure in various domains, such as project management, financial investments, or even personal relationships. Poor decision-making can lead to costly mistakes, damaged reputations, and setbacks that can be difficult to recover from. Since decision-making is not a basic human skill, but the result of the interplay of several skills, a different strategy was used. To define decision-making, we used the database created by Columbia University. The Decision Making Individual Differences Inventory (DMIDI) is a catalogue of over 200 individual difference measures commonly used in judgment and decision-making research. It contains measures about decision style and approach. Measures of decision style assess the ways in which individuals approach decision making, or thinking more generally (e.g., whether individuals adopt a rigorous analytic style or a gut-based experiential style). Measures of decision approach assess individuals’ management of the decision process, both pre- and post-decision (e.g., indecision, regret). The key elements were the following: – Recognition of decisional situations – Information Gathering and Analysis – Option Generation – Decision Implementation |
|
Sub-categories with definition |
Decision-making Skills: Decision-making skills encompass the capacity to assess options, weigh alternatives, and make informed choices based on logical reasoning, critical analysis, and consideration of consequences. Ability to Work Independently: The ability to work independently involves self-reliance, initiative, and autonomy in managing tasks and responsibilities without constant supervision. It includes setting goals, prioritizing tasks, and problem-solving with minimal guidance. Situational Adaptability: Situational adaptability refers to the capability to adjust and thrive in various circumstances or environments. It involves being flexible, resourceful, and responsive to changing conditions, challenges, or demands while maintaining composure and effectiveness. |
|
List of key elements |
– Self-motivation – Time Sharing – Initiative – Resourcefulness – Situational adaptability, we used the scientific literature for creativity and resilience, and defined the following key elements: – Selective Attention – Fluency of Ideas – Originality – Resilience |
|
Utilization of competence elements in work-life |
Decision-making competence elements are integral to navigating both professional and personal realms effectively. In the workplace, individuals rely on these elements to assess situations, weigh options, and make informed choices. This includes factors such as critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and the ability to analyze data. Employees adept in decision-making competence can efficiently prioritize tasks, resolve conflicts, and drive projects forward. Moreover, they demonstrate adaptability and resilience in the face of uncertainty or adversity. Beyond the office, decision-making competence extends to managing finances, relationships, and personal goals. Individuals with strong decision-making skills can allocate resources wisely, negotiate effectively, and make sound choices that align with their values and aspirations. Ultimately, the utilization of decision-making competence elements in work-life fosters success, satisfaction, and overall well-being. |
|
Category title |
Thinking and reasoning |
|
Category definition |
Thinking is a fundamental cognitive process that plays a crucial role in various taxonomies and frameworks within psychology and cognitive science. In the field of cognitive psychology, thinking is often categorized as a higher-order cognitive function alongside other mental processes such as perception, memory, and attention. Additionally, in the realm of decision-making, thinking is an integral component, as it involves the evaluation, analysis, and synthesis of information to make informed choices. To define thinking, we selected the Cattell-Horn-Carroll (CHC) taxonomy as a basis. The Cattell-Horn-Carroll (CHC) taxonomy is a widely recognized and comprehensive model that classifies cognitive abilities. It provides a framework for understanding and assessing various cognitive processes, including thinking. Thinking, as a complex cognitive function, plays a significant role within this taxonomy. Thinking is an integral part of the CHC taxonomy as it cuts across various cognitive abilities. It relies on the integration and interaction of multiple cognitive processes to facilitate problem-solving, critical thinking, and decision-making. The CHC framework acknowledges the complexity and multidimensionality of thinking, highlighting its importance in cognitive functioning. |
|
Sub-categories with definition |
Thinking category consist of three sub-categories: Critical thinking, problem solving, analytic and logical thinking Critical Thinking: Critical thinking is the disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, analyzing, synthesizing, and evaluating information to reach well-reasoned conclusions or decisions. Problem Solving: Problem solving is the systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and resolving challenges or obstacles to achieve desired goals or outcomes. It involves defining the problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating alternatives, and implementing effective strategies. Analytic and Logical Thinking: Analytic and logical thinking refer to the ability to break down complex information into smaller components, analyze relationships, and draw logical conclusions based on evidence and reasoning. It involves applying structured, systematic approaches to problem-solving and decision-making. |
|
List of key elements |
Critical Thinking – Analysis – Evaluation – Inference – Self-reflection and correction Problem solving – Problem sensitivity – Analysis – Solution Generation – Implementation Analytic and logical thinking – Deductive Reasoning – Inductive Reasoning – Category flexibility – Information ordering |
|
Utilization of competence elements in work-life |
Thinking competence elements play a crucial role in work-life by enabling individuals to approach tasks, challenges, and decision-making processes effectively. These elements include critical thinking, creativity, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. In the workplace, critical thinking allows employees to analyze situations, evaluate information, and make sound judgments. Creativity fosters innovation, leading to the development of new ideas, products, and solutions. Problem-solving skills empower individuals to identify issues, formulate strategies, and implement solutions efficiently. Decision-making skills help in assessing options, weighing alternatives, and making informed choices. Together, these thinking competence elements enhance productivity, promote collaboration, and drive success in various professional endeavors. |
|
Category title |
Leadership and organization |
|
Category definition |
The definition of what leadership is has greatly changed through time. Currently, leadership is a process – highlighting the transactional event between the leader and followers, rather than a trait that the leader possesses – in which an individual has influence and power over one or more employees to achieve a common goal. Moreover, leadership encapsulates the ability to inspire, and guide others towards a common goal, thus ensuring a mutual purpose. A strong leader possesses several key features: vision, communication, empathy, decisiveness, and integrity. By articulating a compelling vision, they inspire commitment and foster innovation. Effective communication ensures clarity and alignment within the team. Empathy enables understanding and support for team members, fostering trust and collaboration. Decisiveness allows for timely action and adaptation to challenges. Integrity builds credibility and maintains ethical standards, earning respect and loyalty. Ultimately, adept leadership cultivates a positive organizational culture, enhances team performance, and drives sustainable success. The concept of organization embodies a diverse range of competences essential for excelling in today’s dynamic work environment. Individuals possessing strong organizational competencies demonstrate the ability to function effectively under pressure while maintaining attention to detail and working autonomously. These competencies encompass the capacity to plan, prioritize tasks efficiently, and utilize resources judiciously, including time, finances, materials, and human capital. The core essence of organizational competencies lies in the adeptness to collect, analyze, and organize information systematically. |
|
Sub-categories with definition |
Subcategories are: leadership, organization (other-oriented), self-management To achieve desired goals and to extract the best achievable performance of teams, leadership orchestrates organizational alignment, embraces flexibility, makes informed decisions, fosters effective communication, encourages innovation, prioritizes ethical values, promotes inclusive collaboration, leverages digital tools, and applies strategic thinking for success. Organization enables individuals to effectively manage their time, tasks, and resources. A key aspect is proficient time management, which involves setting priorities and adhering to the deadlines. Adaptability is crucial in navigating unexpected changes, while efficiency and productivity are paramount goals. Self-management is the ability to organize oneself and involves effective networking & communication, creating strategies, personal growth, collaboration, upholding values, mastering digital tools, critical thinking, leading & organizing tasks, adapting flexibly, and making sound decisions, fostering autonomy and productivity. |
|
List of key elements |
Leadership: a range of knowledge and skills in the required field, with a good command of theories and principles governing the topic, a proven track record of good decision making, innovativeness, clear and direct communication, team spirit and a sense of belonging, digital proficiency, critical thinking, complex problem solving, reviewing the strategic performance of teams. Organization and self-management: effective time management, task prioritization, planning and scheduling, goal setting, information management, decision making, adaptability, efficiency and productivity, communication, stress management, self-discipline. |
|
Utilization of competence elements in work-life |
Leadership is crucial at different hierarchical levels and in different industries for guiding teams towards goals. In business. It involves strategic planning, decision-making, and team management. In education, it fosters student development and institutional growth. In politics, it shapes policies and drives societal progress. In healthcare, it ensures patient care quality and staff coordination. Effective leadership cultivates innovation, motivates individuals, and fosters collective success, making it indispensable in every field. Organization is indispensable across diverse industries and professions, including tasks such as project planning, administrative duties, classroom management, software development, and marketing campaigns. In project management, these skills enable efficient allocation of resources, tracking of progress, and adherence to deadlines. Administrative roles rely on organizational skills for managing calendars, coordinating meetings, and handling correspondence. In education, for lessons planning and student record-keeping, while in technology, to prioritize tasks and ensure timely delivery of products. Creative fields such as marketing and design benefit from organization in managing assets and coordinating campaigns. Self-management spans work, study, and personal life, involving tasks such as goal setting, time management, prioritization, and self-reflection. It’s crucial across disciplines for efficiency, productivity, stress reduction, and achieving goals, enhancing performance and well-being. |
|
Category title |
Communication and networking |
|
Category definition |
Communication refers to the process of exchanging information, thoughts, ideas, or feelings between individuals or groups through verbal, non-verbal, or written means. Key features of communication are clear and concise expression of thoughts and ideas, attentive listening, empathy, adjusting communication styles according to the audience and context, non-verbal communication (using and interpreting body language, gestures and facial expressions), providing and receiving constructive feedback to improve it and it is used for addressing conflicts and disagreements through effective communication techniques. The benefits of communication lie in strong interpersonal connections, enhanced collaboration, and increased productivity, because clear communication reduces misunderstandings and streamlines workflows. It helps in career advancement, as communication is often a key factor of career success. It also helps in identifying, analyzing and resolving issues efficiently and brings positive consequences: inspires trust, respect and positive influence on others. Networking involves establishing and maintaining relationships with individuals or groups for mutual benefit, such as sharing information, opportunities, and resources. The features of networking are in actively seeking and forming of new relationships, maintaining relationships, offering support and assistance to others within the network, consistently staying in touch and following up with contacts, exchanging valuable information, insights and resources, and helps create a positive and memorable impression within professional circles. Networking facilitates finding job opportunities, collaborations and partnerships, aids in learning and skill development through information sharing, expands professional horizons and opens doors to advancement, provides access to diverse resources, expertise and support networks, raises visibility and credibility within relevant industries or communities, gives opportunities for mentorship and guidance from experienced professionals, but it also fosters a sense of belonging and fulfillment through meaningful connections. |
|
Sub-categories with definition |
Subcategories are: assertive communication, networking, intercultural competence Assertive communication refers to the ability to speak and interact in a way that respects the boundaries and opinions of others, but also express one’s own rights, needs and personal boundaries. Key elements of assertive communication are: active listening, expressing oneself confidently, persuasion and mastery of assertive techniques. Networking means that individuals are able to create, develop and use interpersonal relationships to mobilize their resources. By resource mobilization, we mean the ability to transform investments in social relationships into social capital, information, resources and other returns that people can use within their social networks. Intercultural competencies are a combination of cognitive, affective and behavioral skills and traits that facilitate interactions in different cultural contexts. Intercultural competencies include various skills: Knowledge, motivation, verbal and non-verbal communication skills, appropriate and effective behaviors. Those who are successful in this area also have ambiguity tolerance, behavioral flexibility, communicative awareness, knowledge discovery, respect for others and empathy. |
|
List of key elements |
Assertiveness workshops: Offer workshops focused specifically on assertive communication skills. Cover topics such as expressing needs and boundaries, handling criticism, and saying no politely but firmly. Conflict resolution training: Provide training on conflict resolution techniques, emphasizing assertive communication as a key component. Teach students how to address conflicts calmly, express their viewpoints assertively, and seek mutually beneficial solutions. Public speaking opportunities: Offer opportunities for students to practice public speaking, such as presentations or debates. Encourage them to communicate their ideas confidently and assertively while respecting others’ perspectives. Feedback sessions: Incorporate regular feedback sessions into coursework or group projects, where students can practice giving and receiving feedback assertively. Emphasize the importance of providing specific, constructive feedback while also being open to receiving feedback from others. Join student organizations and clubs: Participating in clubs related to their field of study or interests provides students with opportunities to meet like-minded peers and professionals. Actively engaging in club activities and events can help students develop their networking skills. Attend career fairs and networking events: Encourage students to attend career fairs, industry conferences, and networking events both on and off-campus. These events often feature representatives from various companies and industries, providing students with valuable networking opportunities. Utilize social media platforms: Advise students to create and maintain professional profiles on platforms like LinkedIn. They can connect with professionals, join industry-related groups, and engage in discussions to expand their professional network. Study abroad programs: Take advantage of study abroad opportunities to immerse oneself in a different cultural environment. Living and studying abroad provides first-hand experience with cultural differences, language immersion, and cross-cultural communication. Language exchange programs: Participate in language exchange programs where students can practice speaking foreign languages with native speakers and learn about their cultures. Language exchanges promote cultural exchange, linguistic proficiency, and intercultural understanding. |
|
Utilization of competence elements in work-life |
Assertive communication plays a pivotal role in contexts such as meetings, negotiations, and conflict resolution. It involves tasks like expressing opinions, setting boundaries, and giving feedback, supported by processes such as active listening, assertive speaking, and managing emotions. This skillset is indispensable for effective leadership, fostering teamwork, and advancing careers across diverse fields, empowering individuals to navigate interactions confidently and cultivate productive relationships. Networking involves tasks like building relationships, exchanging contacts, and seeking opportunities. Key processes include connecting with others, maintaining relationships, and leveraging connections for mutual benefit. Networking is indispensable for career growth, job search endeavors, and accessing valuable resources and support across diverse fields, serving as a cornerstone for professional advancement and success. Intercultural competencies are vital in global business, cross-cultural teams, and multicultural communities, encompassing tasks such as communicating across cultures, resolving cultural conflicts, and adapting to diverse environments. Intercultural competencies are critical for fostering global collaboration, driving diversity and inclusion initiatives, and navigating multicultural environments effectively, ensuring mutual understanding and respect across cultural boundaries. |
|
Category title |
Digital proficiency |
|
Category definition |
Digital proficiency embodies the capacity to adeptly engage with and harness the potential of digital tools, technologies, and platforms. It encompasses a spectrum of skills and competencies enabling individuals to navigate the digital realm effectively. This competence entails a profound understanding of computer systems, software, and networking, empowering individuals to troubleshoot problems and optimize system performance. Moreover, it involves the ability to critically evaluate and utilize digital information ethically, ensuring informed, responsible, and sustainable decision-making and resourcefulness. Proficient individuals communicate seamlessly, synchronically or asynchronously, across various digital channels, fostering collaboration and knowledge exchange to achieve a common objective. They excel in managing and analyzing digital data, extracting insights to inform strategic decisions and problem-solving practices, and driving development and innovation. Additionally, digital proficiency entails a heightened awareness of cybersecurity threats and measures to safeguard personal and organizational data and digital identity. Creativity flourishes as proficient individuals leverage digital tools for innovative content creation and expression. Adaptability and a thirst for continuous learning characterize digital proficiency, enabling individuals to remain agile and responsive to evolving digital landscapes. Moreover, advanced programming skills and an understanding of programming concepts, algorithms, and data structures enable individuals to design efficient and scalable solutions to complex problems, collaborate effectively with team members, and deliver high-quality software solutions on time and within budget. Ultimately, digital proficiency empowers individuals to navigate and excel in the interconnected, technology-driven world of today and tomorrow. |
|
Sub-categories with definition |
Subcategories are: advanced computer handling, collaborating in digital environment, programming Advanced computer handling entails proficiency in managing computer hardware and software systems and enables seamless navigation and utilization of digital resources. Understanding computer architecture allows individuals to troubleshoot problems and optimize system performance. Collaborating in a digital environment uses communication technologies and collaborative software to facilitate digital teamwork, knowledge sharing, and project management. It entails the ability to organize and manage digital files and documents, share resources securely, and engage in real-time cooperation with remote team members. Programming involves understanding, creating, testing, and debugging computer programs. Advanced programming skills encompass a deep understanding of algorithms, data structures, programming frameworks, and libraries. Proficiency in software development methodologies allows programmers to deliver high-quality software on time and within budget. |
|
List of key elements |
Technical literacy: a deep understanding of various digital technologies, hardware, and software systems. Information literacy: skills that enable individuals to find, evaluate, and use digital information effectively and ethically. Digital communication skills: strong communication skills across all digital platforms, enabling individuals to express ideas clearly and effectively in a variety of digital formats. Data management: the ability to manage and manipulate digital data efficiently and securely. Cybersecurity awareness: awareness of cybersecurity threats and best practices for protecting personal and sensitive data online. Digital creativity: enable individuals to utilize digital tools and platforms to create engaging content, multimedia presentations, and digital artwork. Problem-solving skills: enable them to identify, analyze, and solve complex problems using digital tools and technologies. Adaptability: willingness to learn and adapt to new technologies and digital trends, keeping up to date with new technologies, and embracing changes in the digital landscape. Collaboration: working with others in digital environments and encouraging teamwork, knowledge sharing, and collaboration across geographical boundaries, using virtual collaboration tools, project management, etc. Continuous learning: a lifelong learning process that requires individuals to continuously update and expand their skills and knowledge in response to evolving technologies and digital trends. |
|
Utilization of competence elements in work-life |
Digital proficiency is indispensable across a multitude of contexts, tasks, processes, and practices in various areas of expertise. In workplaces, adept digital skills facilitate efficient communication, collaboration, and task management through the use of digital tools and platforms. Education relies on digital proficiency to access online resources, participate in virtual learning environments, and facilitate remote instruction. Digital proficiency is crucial in creative industries for content creation, graphic design, and multimedia production. Businesses leverage digital proficiency for marketing, e-commerce, data analytics, and customer relationship management. Government agencies depend on digital skills for public administration, policy development, and citizen engagement. In essence, digital proficiency is paramount across diverse fields as it fosters efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness, enabling individuals to navigate the complexities of the digital age and excel in their respective domains. |
|
Category title |
Collaboration |
|
Category definition |
These skills refer to the ability to convey information (orally and in writing) clearly and transparently, to listen to others and to understand their needs. They describe the ability to flexibly adapt the form of communication to different audiences. They indicate the ability to create an atmosphere of openness, striving for agreement by working out solutions that are satisfactory to each of the parties involved. On this basis, it is possible to draw conclusions about the person’s ability to establish positive relationships with others, the awareness of his/her own role and the impact of actions taken on the team’s overall performance. Interpersonal skills manifest themselves in activities that improve and facilitate the achievement of common goals through the sharing of knowledge, experience and information. They include elements such as providing support, being open to other people’s ideas, opinions and feelings, and being able to put the group’s decisions before one’s own interests. Collaboration competence refers to the ability to effectively work and communicate with others towards a common goal. It involves skills such as active listening, clear and respectful communication, empathy, problem-solving, flexibility, and the ability to contribute and receive feedback. Collaboration competence is essential in diverse settings, including work environments, teams, projects, and partnerships, as it promotes synergy, productivity, innovation, and positive relationships among individuals or groups. |
|
Sub-categories with definition |
Teamworking: The ability to work in a team means being able to actively listen to other team members, being able to follow their instructions, and also being able to clearly communicate our viewpoint and instructions to other members. It also means enhancing one another’s strengths. Working in a diverse team: To be open to other cultures and to alter the communication style and to be aware of the diversity. Interpersonal skills when working in a diverse team consisting of members from different cultures, generations and possibly with disabilities, as well as displaying appropriate attitudes in this respect. Presenting and public speaking: Ability to speak to a group of people in a formal or informal setting to inform, persuade, or inspire an audience using verbal communication (language), non-verbal communication (tone and body language), and visual aids (e.g., slides, charts, multimedia). |
|
List of key elements |
Sub-category: Teamworking Ability to cooperate Learning from others Focus on goal Sub-category: Working in a diverse team Generational diversity Functional diversity Cultural diversity Sub-category: Presenting and public speaking Language skills Non-verbal communication Presentation skills |
|
Utilization of competence elements in work-life |
Collaboration facilitates and increases the effectiveness of team cooperation, influences effective communication, good exchange of information, stimulates the level of motivation (both individual and group), facilitates the planning of activities and accelerates decision-making processes. It is the basis for the efficient implementation of group professional tasks in teams of employees diverse in terms of generation, functionality and culture. It also allows you to manage a task or project, assign roles and responsibilities to individual team members, take into account alternative perspectives, prevent and resolve conflicts. |
|
Category title |
Personal development |
|
Category definition |
Personal development is a lifelong process of increasing self-awareness, acquiring new skills and actively striving for continuous improvement. It is closely related to an individual’s ability to effectively manage and develop oneself, encompassing skills, knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors that contribute to personal growth, adaptability, self-awareness, and overall effectiveness in various aspects of life. Other definitions of personal competence may emphasize slightly different aspects, but they generally revolve around an individual’s capacity to navigate and excel in personal and professional domains. Personal development is the process of realizing your capabilities, unlocking your potential and achieving your personal and professional goals. Some alternative definitions may highlight specific components such as problem-solving skills, emotional intelligence, self-motivation, resilience, interpersonal effectiveness, or the ability to learn and adapt to new situations. However, the overarching concept remains focused on an individual’s capability to manage themselves effectively and thrive in different contexts. A personal development framework may include goals or benchmarks, strategies or plans to achieve goals, measurement and evaluation of progress, levels or stages that define milestones along the development path, and a feedback system regarding milestone achievement and changes as they occur. Personal development can be achieved through self-education, coaching, mentoring and training. |
|
Sub-categories with definition |
Learning skills – openness to constant development and easy adaptation to changes; ability to organize one’s own learning process, including effective management of time and information, both individually and in groups; the awareness of one’s own learning process and own needs in this respect. Self-reflection – this competency means to know your own value, positive and negative side, your strength and weaknesses; ability to evaluate yourself, be aware of the own characteristics, to consciously observe yourself. Openness – open-mindedness, to be open to new ideas, opinions, new arguments, innovations, new ways of doing things and new perspectives. Despite popular belief we cannot live and work in isolation, so we have to be open to meet people, listen to people, and accept people with views and values differing from ours. |
|
List of key elements |
Sub-category: Learning skills Openness to development Learning process management Ability to learn Sub-category: Self-reflection Ability to observe and evaluate cognitive processes Ability to observe and evaluate emotional states Ability to observe and evaluate behavioural processes Sub-category: Openness Curiosity and perceptiveness Openness to experience Taking up challenges |
|
Utilization of competence elements in work-life |
Personal development includes activities that raise awareness, shape identity, build self-esteem, mental strength, increase adaptability and develop talents and potential. These activities include self-education, training, courses, internships, as well as mentoring and coaching. Personal development contributes to the realization of aspirations and plans and improves the quality of life. Effective implementation of personal development goals is based on learning skills, self-reflection and openness. |
|
Category title |
Ways to create |
|
Category definition |
To make it clear that you can offer added value in the field of creativity based on your experience, it is useful to consider the following key-aspects of creative ways of thinking and refer to them in your review;
|
|
Sub-categories with definition |
Creativeness Generating new ideas, creative style of work; come up with new ideas, Consider other ways or scenario’s to deal with problems, use professional space given by management. Proactiveness Coming up with suggestions, Placing new tasks in a broader perspective, Prepare yourself to new tasks, Coming up with innovative concepts. Innovativeness Introducing new relevant partners, Coming up with new concepts |
|
List of key elements |
Creativeness Assessing opportunities Generating new ideas Discovering new connections Exploiting new ideas Proactiveness Foreseeing problems Solution focus Motivating others Innovativeness Initiative Embracing development Utilizing connections |
|
Utilization of competence elements in work-life |
Related Contexts, Company strategy is always renewing itself sometime by vision and mission of the management but also by development in the community. This business strategy takes not only the management into account but also all employees. So it is important to keep up with the rest of your organization and anticipate on changes lying ahead. Related Tasks, Strategical changes lead to new tasks and new handling and behavior it is important to deal with this kind of change and develop new ideas and concepts but also learning to deal with quick changes. Related Processes, New ideas and concepts lead to new capabilities, other competences, skills and knowledge it is important to keep up with the latest developments in the market, to stay curious and foresee what trends are coming up that suits your career and the organizational growth. Related Practices, Creativeness is needed to follow up all kinds of new developments, organizational and personal but they don’t lead to result if you cannot put it to practice. So it is important to make new concepts or ideas practical by giving it structure and meaning for those who need to follow up |
Learning Path Definitions
|
Name of LP |
Animal care (pets) |
|
Island of LP |
Home |
|
Definition |
Animal care is a set of activities aimed at providing animals with living conditions that meet their physiological, behavioral and health needs. Its activities include, among others: regular feeding, access to fresh water, providing adequate space for movement and activity, veterinary care, health checks and providing an appropriate environment and socialization conditions. Pet grooming is the practice of caring for the hygiene, health and appearance of animals. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
By caring for animals, we develop skills such as empathy, observation, time management, problem solving, interpersonal communication, self-discipline and patience. These competencies can be useful in various professional fields, from working with people in the health care or education sectors, to industries related to customer service, human resources management, the veterinary, zoological and breeding industries, as well as in environmental protection and animal rights organizations. |
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.) Taking care of animals can teach us valuable skills related to rest and relaxation, which can be beneficial to our mental health and overall well-being in our personal lives. It can also teach us how to combine work with pleasure and enjoy simple activities, which can contribute to a better balance in our personal lives. These skills will definitely be more useful in your personal life than in your professional life. |
|
Name of LP |
Competitions/ races/ professional sports |
|
Island of LP |
Sport |
|
Definition |
Professional sports are professional sporting activities in which athletes or teams compete at the highest level, often earning money from their sporting activities. Professional athletes often participate in regular leagues, tournaments, and competitions, earning financial rewards or other forms of compensation for their achievements. Participating in a championship means competing in sports competitions at the highest level, often representing a country, region or club. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
Practicing professional sports and participating in championships develops a number of skills and competencies that can be very useful in professional life, including: discipline, punctuality, accuracy, motivation and perseverance, stress management, teamwork, time management and relationship building, as well as responsibility, competition and fair-play rules – can be beneficial in building a network of contacts and business relationships in professional life. Some competencies and skills developed while practicing professional sports and participating in championships may be more useful in personal life than in professional life. These are: passion and commitment, the ability to accept failures, building relationships and social bonds and managing emotions. |
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.) Occasional sports, jogging, playing sport just for fun at home, etc. |
|
Name of LP |
Training and onboarding new colleagues |
|
Island of LP |
Work |
|
Definition |
At a time when it is becoming increasingly important to find and, above all, retain new employees, onboarding and training play an important role in recognizing and supporting unique talents, especially within the context of an organization. A company where employees are leaving again after a few months is saddled with enormous costs, not only of recruitment but also of the introduction, training and salary, but also the ‘temporary’ pressure on the rest of the organization has its price. In addition to enthusiasm, matters such as addressing responsibilities and personal behavior are also important. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
|
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.)
|
|
Name of LP |
Family business member (early experiences) |
|
Island of LP |
Work |
|
Definition |
Family businesses are often seen as the backbone of the national economy. Coming into contact with this at an early stage clearly shapes young people. They understand the ‘seriousness and fun’ of the business and know how to deal with different clients and customers. This is often accompanied by expert knowledge, but that is not a ‘must’. In addition to this knowledge, doing business also consists of making contacts and being able to assess their value, a personal approach to conversation partners, and being able to distinguish between ‘social talk’ and the more business side of collaboration. Working in a company offers you the opportunity to develop a sense of business. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
|
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.)
|
|
Name of LP |
Home nursing |
|
Island of LP |
Health |
|
Definition |
Due to the aging population, more and more young people are coming into contact with caring for parents or grandparents, informal care. This varies from helping to prepare food, shopping, but also light paramedical and supporting tasks such as putting on support stockings. In addition, it demands a lot from the family in terms of administration and applications for permits and subsidies. Core values are loyalty, caring, connection, involvement and love. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
Supporting competencies are;
|
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.)
|
|
Name of LP |
Special needs (allergies, injuries, states of minds – own or family member) |
|
Island of LP |
Individual |
|
Definition |
This learning path aims to develop the individual’s attitude, knowledge, and skills to deal with any of special needs (allergies, injuries or states of minds – own or family member) and to avoid their negative effects on daily life, including their effects on physical health, mental well-being, and the ability to participate in social, educational, or professional activities. It includes activities as searching information about special needs, conversation with other people with special needs, reading professional and educational books, offering support, sharing experiences to people who are only at the beginning of the learning process, informing family members and colleagues how to help in emergency cases. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
Learners will focus on developing a diverse set of skills tailored to effectively manage and support special needs. Key competences include:
|
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.) It’s important to understand that while this path aims to be comprehensive, it:
|
|
Name of LP |
Healthcare (own diet and fitness) |
|
Island of LP |
Health |
|
Definition |
Healthcare (Own Diet and Fitness) focuses on individual responsibility for personal health, encompassing nutrition, exercise, and overall well-being. The learning path includes educational resources, goal setting, nutritional guidance, exercise programs, tracking tools, community support, expert guidance, behavioral strategies, and technology integration. Activities involve reading, participating in discussions, completing assessments, following workout plans, tracking food and exercise, setting goals, seeking guidance, and utilizing technology for learning and communication. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
Activities within the learning path support various competencies essential for success in work-life, including:
|
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.) The Healthcare Learning Path does not cover medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment for specific health conditions. It excludes content on extreme dieting, supplements not approved by healthcare professionals, and high-risk fitness activities without proper supervision. Additionally, this path does not encompass mental health therapies or treatments that require professional healthcare consultation. It’s designed for educational purposes with a focus on promoting general wellness through diet and fitness, not substituting professional healthcare services. |
|
Name of LP |
E-gaming / E-sport |
|
Island of LP |
Play |
|
Definition |
An E-gaming/E-sport learning path is an educational journey focused on developing skills and knowledge in electronic gaming and competitive gaming (e-sports). It blends theory with practice, emphasizing strategic thinking, teamwork, and problem-solving. Features include:
|
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
|
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.) The E-gaming / E-sport Learning Path does not cover gambling, betting, or any forms of financial speculation related to gaming events. It excludes non-competitive casual gaming, traditional sports, and activities not directly related to electronic gaming or e-sports. The path also omits the development of gaming software or hardware technicalities. Its primary focus is on skill development, strategic thinking, and teamwork within the e-sports and competitive gaming arena. |
|
Name of LP |
Role playing games / board gaming |
|
Island of LP |
Play |
|
Definition |
Role playing games / board gaming learning path is a structured approach to developing skills and knowledge in role-playing games (RPGs) and board gaming. It involves a series of activities designed to introduce participants to various aspects of these games, deepen their understanding, and foster growth in areas such as strategy, critical thinking, teamwork, and creativity. Features and typical practices of such a learning path may include:
|
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
|
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.) The Role Playing Games / Board Gaming Learning Path does not encompass video gaming or electronic-based gaming activities. It excludes gambling-related board games or any activities involving betting. The path focuses solely on skill development and enjoyment through tabletop RPGs and board games, excluding the collection or appraisal of rare or vintage games. |
|
Name of LP |
Singing/instrument playing/orchestra/band concerts |
|
Island of LP |
Art |
|
Definition |
Singing is an activity in which an individual or a group produce musical sounds through the use of their vocal cords, lungs, and mouth. Playing an instrument refers to the act of performing music on a specific instrument. It includes activities as performing music for audiences and recordings; audition for positions in orchestras, choirs, bands, other types of music groups; practice playing instruments or singing to improve their technique; rehearse music and parts to prepare for performances. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
Solo singing and playing an instrument develops self-control, perseverance, accuracy and responsibility. In a choir or being a member of an orchestra contributes to the development of group work, listening to each other and relationship-building skills also. Public performances improve confidence. Meeting performers of other nationalities can also develop intercultural competences. Music is about time signatures and beats per minute so performing music reinforces parts of the brain used when doing math. |
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.) Engaging in music can have positive effects on mental health, reducing stress and anxiety which may be more useful in personal life. The choir and the orchestra have the interests of the ensemble as a whole at heart, so they do not support individual fulfilment and self-management. The requirements of the score and the rest of the ensemble can limit the expression of creativity. |
|
Name of LP |
Event planning |
|
Island of LP |
Work |
|
Definition |
Event planning is the process of staging and managing a variety of public and private events for social or business purposes, ranging from family occasions to small meetings and large conventions. Event planning includes ensuring that every aspect of the event is well thought-through and meticulously planned and flawlessly executed. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
Even planning includes numerous tasks, depending on the type and scale of the event. Most typical planning activities are:
Not every event will include all the tasks above. However, due to the complexity of tasks involved, engaging in event planning will develop organizational skills, attention to detail, creativity, problem-solving, flexibility, time management and stress management abilities. |
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.) Planning routine tasks Planning activities involving just one or a few other people, getting together without specific goals and objectives |
|
Name of LP |
Student exchange / volunteering abroad |
|
Island of LP |
Community |
|
Definition |
Student exchange entails students temporarily swapping places between educational institutions in different countries, fostering cultural exchange and language acquisition. Volunteering abroad involves offering time and skills for community betterment, promoting empathy and social responsibility. Both provide immersive experiences for personal growth, intercultural competence, and global citizenship. These experiences often occur through formal programs like Erasmus, EVS, and EEAS etc., which offer clear objectives, ensuring safety, support and expertise. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
|
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.) Personal travel unrelated to the exchange or volunteering program. Non-approved volunteer activities or projects. Participation in illegal activities and its expenses. Incidents occurring outside the designated exchange or volunteering period. |
|
Name of LP |
Photography / video making and editing |
|
Island of LP |
Art |
|
Definition |
Photography is the art, application, and practice of creating images by recording light, either electronically or chemically. Video art is an art form which relies on using video technology as a visual and audio medium. These art forms include composing and shooting frames and scenes with the intention to express feelings, broadcast views or tell stories. Any equipment / technology can be used, but the intention of sharing or publishing is required. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
Planning, staging and recording a given concept Light, space, sound and motion perception and the use of physical dimensions in imaging and recording Identifying and highlighting substantive elements, epiphany Build up a message, utilizing the art piece as a medium to transfer thoughts and feelings Self-expression and self-realization |
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.) Shooting and archiving daily routines or family occasions for personal or family use Making digital copies / recordings of documents, information, lectures, notes, etc. for study purposes or just to remember them Private or sensitive pictures and videos AI generated images or video |
|
Name of LP |
Home responsibilities (chores, repairs, maintenance) |
|
Island of LP |
Individual |
|
Definition |
Home responsibilities encompass a range of activities aimed at teaching individuals the necessary skills to effectively manage household chores, repairs, and maintenance tasks. This learning path aims to equip individuals with the skills, knowledge, and attitudes needed to effectively manage household tasks and contribute to a functional and harmonious home environment. Activities include cleaning, laundry, meal preparation, gardening, home maintenance, organization, financial management or emergency preparedness (in case of fire, flood or other emergencies). |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
Competences developed through the above mentioned activities are the following:
|
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.)
|
|
Name of LP |
DIY / Home renovation |
|
Island of LP |
Home |
|
Definition |
Do-it-yourself (DIY) and home renovation activities encompass a broad range of features and practices centered on improving, repairing, or enhancing residential spaces without professional assistance. Typical preparation activities include designing renovation projects, planning activities and buying materials. Typical renovation activities include painting, wallpapering, installing flooring, tiling, carpentry, plumbing, electrical work, and landscaping. Projects include furniture assembly, wall repairs, fixture replacements, and minor home improvements. These endeavors may involve tasks like sanding, staining, drilling, measuring, sawing, and hammering. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
Competences developed through the above mentioned activities are the following:
|
|
Exclusions |
|
|
Name of LP |
Team Leader (work experience) |
|
Island of LP |
Work |
|
Definition |
Team Leader (Work Experience) includes activities that focus on developing leadership skills, communication skills and the ability to motivate and lead a team to achieve common goals. Activities include communicating to ensure clear understanding and alignment within the team, delegating tasks to optimize team strengths, setting strategic goals to drive team focus and success, improving conflict resolution skills to maintain a harmonious team environment, as well as making decisions under pressure to guide the team through challenges. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
Competences developed through the above mentioned activities are the following:
|
|
Exclusions |
|
|
Name of LP |
Self-development/Self-help activities |
|
Island of LP |
Individual |
|
Definition |
Self-development is a structured and personalized approach to personal growth, encompassing goal setting, diverse learning modalities, progress tracking, reflection, consistency, community support, holistic development, adaptability, and celebration of achievements. Activities include goal setting, self-assessment, curriculum design, progress tracking, reflection and adjustment, and celebrating milestones. Broadly, self-development includes also traveling, experimenting with different selves, and practicing body-mind awareness-enhancing modalities. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
Competences developed through the above mentioned activities are the following:
|
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.)
|
|
Name of LP |
Language clubs / presentation club / debate club |
|
Island of LP |
Community |
|
Definition |
Language clubs are groups of learners of a foreign language who meet (online or in person) to practice their communication skills in a particular foreign language, make contacts and participate in cultural events and programs related to the country of the target language. Presentation and debate clubs are associations aimed at improving skills in public speaking, presenting, communicating, persuading and motivating others. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
Active participation in language clubs improves the ability to communicate and carry out professional tasks in a linguistically diverse environment. Presentation and debate clubs develop skills in presenting and communicating effectively to others, discussion and debate skills, the ability to argue, persuade and motivate others, influence the ability to adapt communication to different professional contexts and diverse audiences. They also increase self-awareness, confidence and self-esteem. |
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.) Passive club membership – failure to demonstrate/confirm interaction and communication in a foreign language (language clubs), 2. Preparation and presentation of a presentation to a wider group of people (presentation club), 3. Generally engaging in debate with random people, active participation in a discussion or debate, taking a stand against the opinions of others, giving feedback (debate club). |
|
Name of LP |
Team play/ team sports |
|
Island of LP |
Sport |
|
Definition |
Team sports are sports disciplines in which competitors must work together as a cohesive team in order to achieve success. Cooperation, communication and synchronization of actions are crucial to achieving goals in these types of sports. A team game is a type of game in which participants work together to achieve specific goals or win. In team games, each player has a role or task to perform, and success depends on effective cooperation and coordination of activities among team members. |
|
Utilization of elements in work-life |
Practicing team sports develops a number of skills and competences that can be very useful in professional life. These include: cooperation and the ability to work in a team, the ability to cope with stress, time management, leadership and motivation to act, problem solving, responsibility for the team and its individual participants, as well as the ability to self-discipline, reflection and a holistic approach. |
|
Exclusions |
(Items or activities specifically not covered in the LP.) Some competencies developed while practicing team sports may be more useful in your personal life than in your professional life. These include, for example: the ability to cope with failure, the ability to accept, the ability to compromise, the spirit of competition and building social bonds – these social relationships can contribute to a greater sense of belonging and support in your personal life. |